TVs are large, loud and bright, so you might be concerned that they use a lot of electricity. If you’re looking to reduce your energy usage to save money and help the environment, then it’s wise to know how much electricity your TV uses and how you can reduce that.
We conducted a study of 227 of the most energy-efficient TVs to bring you the latest and most accurate data about TV power consumption.

In this guide, we’ll explain how much electricity each type of TV uses. There’s also a handy calculator so that you can work out exactly how much your particular TV-watching habits are contributing to your rising electricity bills.
Key Findings:
- Modern TVs use an average of 56.7 watts when turned on and 1.6 watts when on standby.
- The most energy-efficient TVs use just 10 watts when turned on
- Older and larger TVs often use over 100 watts
- The average 55-inch 4K LED TV uses 68.4 kWh of electricity per year, costing $9.58
The most energy-efficient TV models are listed below.
How Many Watts Does A TV Use?
Most TVs use between 27 watts and 134 watts of electricity when they are turned on and about 1 watt of electricity in standby mode. The actual amount of power used depends on the type of TV, the screen size, and the resolution, but the average TV uses 57 watts.
The trend for larger, brighter 8K TVs has meant that newer TVs generally require more power to function than those that were made a few years ago.
The wattage of a TV is affected by:
- TV type – Old plasma TVs use the most electricity
- Screen size – The larger the screen, the higher the wattage
- Resolution – 8K ultra high definition screens use the most electricity
- Settings – e.g. brightness or energy-saving mode
Let’s look at these factors in more detail, along with the average wattages of TVs using various settings…
Some Types of TVs Use More Power Than Others
There are seven different types of TVs in existence. This list explains the technology behind TVs, from newest to oldest.
- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) – Manufactured by LG, these TVs use a new technology with millions of light-emitting pixels
- QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) – Made by Samsung, Sony, and others, these TVs are similar to LCD but with extra molecules called quantum dots
- LED (Light Emitting Diode) – The most common type of TV today, these have light-emitting diodes instead of standard cold-cathode fluorescent lights
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) – Now being replaced by newer tech, these TVs use a unique state of matter called liquid crystals
- Plasma – The first-flat screen TVs, these use small cells containing ionized gas
- DLP (Digital Light Processing) – These chunky flat-screen TVs were produced until 2012
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) – These are the old-fashioned box TVs that are pretty rare to see nowadays
LED TVs are the most energy-efficient televisions, using around half of the energy of LCD TVs. The newest OLED and QLED TVs tend to use around 50% more energy than LED TVs because they’re usually larger with a higher resolution.
Old technology like plasma, DLP, and CRT are the least energy-efficient so it’s worth upgrading these to newer models. Large plasma TVs require the most electricity to run of all TVs.

The Larger The Screen, The More Electricity The TV Uses
The screen size of a TV is measured diagonally from corner to corner. Unsurprisingly, larger TV screens require more power than smaller ones.
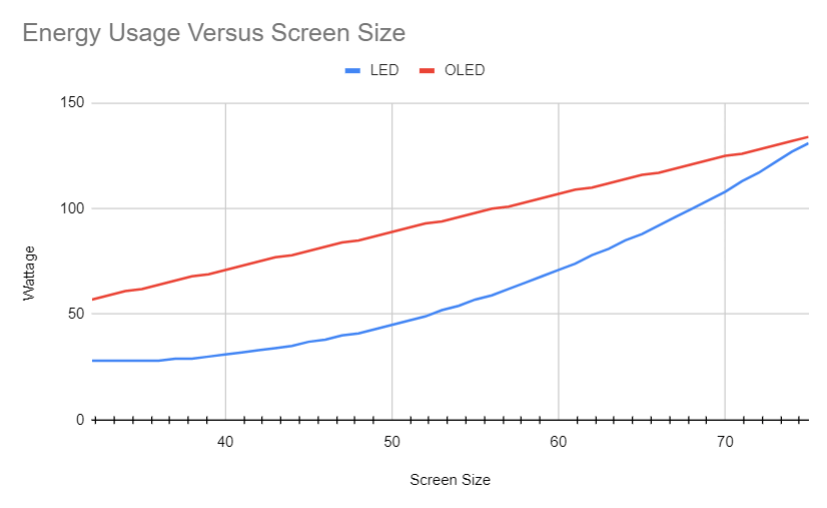
Using data from tests with watt-meters, this table shows how larger TV screens require much more energy than smaller ones:
| Screen Size (inches) | LED TV | OLED TV |
|---|---|---|
| 32 | 28W | 57W |
| 50 | 45W | 89W |
| 55 | 57W | 98W |
| 65 | 71W | 107W |
| 75 | 131W | 134W |
The graph below demonstrates that with OLED TVs, the screen size is directly proportional to the wattage. However, with LED TVs, once you go larger than 60 inches, the energy-efficiency benefits start to lessen.
HD TVs Use More Energy Than Those With Lower Resolutions
High-definition TVs have more pixels than standard-definition TVs. This creates a sharper image, but also requires more energy.
The most common TV resolutions are:
- 720P – Older, smaller TVs use this resolution but you won’t generally find it with new TVs
- 1080P Full HD – An economical choice, this is the resolution of many cheap TVs
- 4K Ultra HD- The most common resolution for new TVs in 2022
- 8K Ultra HD – With 16X the resolution of full HD, these TVs are very expensive
8K TVs generally require a lot more power than 4K TVs because they have four times as many pixels.
This table shows the average wattage for different screen resolutions:
| Screen Resolution | Average Wattage |
|---|---|
| 720p | 28W |
| 1080p | 34W |
| 2060p | 80W |
| 4K | 222W |

8K TVs can often get very hot, something that doesn’t often happen with 4K TVs. If you live in a hot climate, heat from your TV will likely increase the amount that you spend on air conditioning.
The Settings On Your TV Can Affect Energy Consumption
The maximum power consumption of a TV can be more than three times its average power consumption. So if your TV is listed as using 115 watts, it could actually use as much as 427 watts on full brightness and volume.
In Europe, TV energy labels now include the energy usage for both SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) and HDR (High Dynamic Range).
Here are the settings to check on your TV:
- Brightness – The backlight is the biggest drain on your TV’s power, so it’s good to turn the brightness down when the room is dark. Some TVs can do this automatically with an Automatic Brightness Control (ABC) or Energy Saving Mode
- High Dynamic Range Mode – This boosts image quality with better contrast, brighter highlights, and deeper colors, but it also increases energy consumption
- Store Mode – Sometimes called Retail Mode or Demo Mode, this is appropriate for the bright lights of a TV store but is inappropriate for home viewing and it will make the energy usage soar so be sure to turn it off
- Sleep Timer – If you regularly fall asleep in front of the TV, program it to turn off after a certain amount of time so it’s not on while you’re asleep

Working Out How Much Electricity Your TV Uses
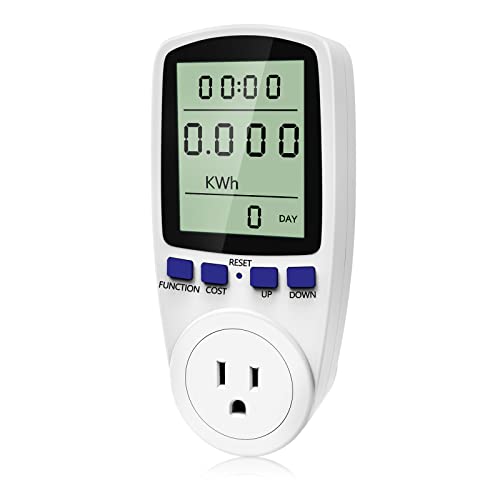
To find out roughly how much energy your TV uses, you can look at the label on the back. Look for a wattage number which is marked with a W at the end. This will tell you how many watts of electricity your TV uses in an hour.
However, if you want to know the exact amount of electricity used by your TV you can buy a cheap wattmeter. You plug your TV (or any other electrical appliance) into this device and it will show you exactly how much electricity it’s using.
A wattmeter can be helpful if you want to know how the different settings affect energy consumption. It’s the best way to work out exactly how much you’re spending over a certain period of time.

How Much Electricity Does A TV Use Per Hour?
The average 55-inch 4K LED TV uses 57 watts of electricity which equates to 0.057 kWh per hour. However, a smaller 32-inch LED TV will use less than half of that at 27 watts and a large 75-inch OLED TV will use more than double with around 134 watts.
The cost of all of this electricity can be high, particularly if the TV is on for many hours each day, if you have more than one TV in your house, or if you live in an area with high electricity rates.
Suggested read: How Big Is A 55-Inch TV?
How Much Electricity Does A TV Use Per Month?
Estimates suggest that the average person spends 3 hours and 17 minutes per day watching television. This equates to 100 hours per month.
The average TV (55-inch 4K LED) will use 5.7 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per month. However, a smaller 32-inch TV will use 2.7 kWh and a large 75-inch OLED TV will use 13.4 kWh.
How Much Does A TV Cost In Electricity?
To work out how much it costs to power a TV, we need to know the TV wattage and the cost of electricity.
Electricity is priced per kilowatt-hour (kWh). 1 kWh of electricity will power a 1000-watt appliance for one hour.
As we learned earlier, TVs use between 27 and 134 watts of power, with the average being 57 watts.
To work out how much it costs to power a TV for an hour, we can use this formula:
(TV Wattage / 1000) X Energy Rate Per kWh
The cost of electricity varies depending on where you live. The average electricity rate in the US in 2022 is $0.14 per kWh. However, it can be as high as $0.34 in some states.
You can out how much you’re paying per kWh for electricity by looking at your bill, or get an average for your state here.
Based on an average cost of electricity in the US of 14 cents per kWh, the average TV will cost 0.8 cents per hour to run. However, a smaller TV will cost only 0.3 cents per hour and a larger TV will cost as much as 1.9 cents per hour.
You can use the following calculator to work out how much your particular TV costs in electricity…
How Much Electricity Does A TV Use on Standby?
When you turn off your TV using the remote control, it doesn’t turn off completely. Instead, most TVs go into ‘standby mode’- they are ready and waiting to come on again. You can tell that a TV is in standby mode because it will have a small red light at the bottom corner.
TVs that were made before 2006 used to consume a lot of power in standby mode, yet manufacturers have worked to improve this and it isn’t so much of a problem with modern TVs. So, if your parents berate you for leaving the TV in standby mode, they may just have outdated information.
Read more: Does Leaving The TV On Waste Electricity?
That said, all TVs do still consume some energy in standby mode. However, the actual costs are minimal so by turning your TV off at the wall you make any noticeable difference to your energy bill.
The average TV will use around 1 watt of electricity per hour when in standby mode, although this varies from 0.5W to 3W depending on the TV. If left in standby mode for 20 hours per day, the electricity would cost around 9 cents per month.
The Best Energy Efficient TVs
If you’re looking for a new TV that scored well in energy ratings, these are some of the most energy-efficient TVs to buy right now.
1. TCL 3 Series
This affordable LED Smart Android TV uses as little as 24 watts of power for the 32-inch version. It has Google Assistant and Chromecast built-in so you can search for movies and shows across thousands of apps.

2. Samsung Q60T QLED
This modern TV has 4K of resolution and used new QLED technology yet uses only 36 watts of power for the 43-inch version. It comes in sizes up to 85 inches and has the digital assistant Alexa built-in.

3. Hisense R6090G
For the best combination of price, functionality, and energy efficiency, you can’t go wrong with this 4K LCD TV that uses just 41 watts of electricity for the 43-inch model. It comes with Roku built-in for easy access to over 5,000 streaming channels and 500,000 movies and TV episodes.

Full List of Energy Efficient TVs
Here’s a list of the best energy-efficient TVs for each screen size, based on the lowest wattage models.
| Screen Size | Make and Model of TV | Wattage | Annual electricity usage |
| 17 inch | Sceptre – E18 | 10W | 19.6 kWh |
| 19 inch | RCA – RT1971-AC | 15W | 28.8 kWh |
| 24 inch | VIZIO – D24hn-G9 | 17.6W | 35.6 kWh |
| 32 inch | MI – L32M5-5ARU | 19.3W | 29 kWh |
| 40 inch | IMPECCA – TL4000F | 31.1W | 58.8 kWh |
| 43 inch | Sansui – S43P28FN | 34W | 66 kWh |
| 50 inch | SCEPTRE – H50 | 47.9W | 88.8 kWh |
| 55 inch | MI – L55M5-5ARU | 62.9W | 92 kWh |
| 65 inch | NEC – E657Q | 72W | 141.1 kWh |
| 70 inch | PHILIPS – 70BFL2114/27 | 109.1W | 205 kWh |
| 75 inch | VIZIO – E75-F1 | 87.3W | 165.7 kWh |
Does A Television Use A Lot of Electricity?
Modern TVs don’t use a lot of electricity with the average TV costing $0.79 per month to run. You can expect a TV to account for less than 1% of your total home electricity bill.
In 2020, the average U.S. household spent $125.09 per month on electricity, with the average U.S. resident consuming 893 kilowatt-hours per month, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Other systems such as heating, cooling, and lighting will use far more electricity than your TV. However, if you do want to reduce your energy consumption and pay less for electricity, there are some ways that you can do this.
- Always turn off your TV when you’re not using it
- Unplug your TV at the wall rather than turning it off with the remote control
- Reduce the brightness of your screen to only the level that’s needed
- If using the TV to listen to the radio, set the screen to be black
- If your TV has an ambient light sensor (ABC), make sure the feature is enabled
- When buying a new TV, choose an energy-efficient model, looking out for the ENERGY STAR label
TV Energy Usage FAQs
On average, 4K TVs use 30% more electricity than 1080P HD TVs, but only half as much as 8K TVs. The higher the resolution of your TV, the more energy it will consume.
The average TV will use 0.456 kWh of electricity if it’s left on for eight hours overnight. This would cost around 6 cents in electricity based on the average rate of $0.14 per kWh.
Unplugging a TV will save some electricity. But unlike TVs of the past, modern TVs are very energy-efficient when left in standby mode. Unplugging your TV will likely save you less than 10 cents per month on your energy bill.
TVs use significantly more electricity than radios. The average TV uses 57 watt-hours whereas the average DAB radio uses 5 watt-hours.
If you listen to the radio on your TV with a black screen, it will use less energy than it would to watch a movie or TV show.
With an average consumption of 57 watt-hours, a TV uses around the same amount of energy as a traditional incandescent 60-watt lightbulb. However, a modern LED lightbulb of the same brightness uses just 6 watts – much less than any TV.
Laptops use 20 to 50 watts of electricity, whereas TVs use between 30 and 130 watts. Therefore, TVs generally use more electricity than laptops do, but there may be exceptions for some very efficient TVs with small screens.
Related Posts:
Useful resources and sources of data for this study:
- https://www.rtings.com/tv/tools/table/
- https://www.energystar.gov/sites/default/files/asset/document/1_Noah%20Horowitz_Ultra%20High%20Definition_FINAL.pdf
- https://www.interdigital.com/white_papers/the-sustainable-future-of-video-entertainment
- https://www.energystar.gov/productfinder/product/certified-televisions/results
